

| RUS |
|
|
|||||||||
The optimal 2-machine configuration of communications between the integrated observational databank ODA-R and the data acquisition systems of the radio telescope RATAN-600 is described. The structure of divisions of the information system, the types of archives and the technology of filling different archive bases with experimental material are discussed. An additional archive statistics for the central Rr-division of the databank is given.
The existing components of the SAO RAS distributed information-computer network and a project of the regional network are described. Realization of the multi-bound network structure improves reliability of the Internet channel connection which is used for scientific researches carried out in the observatory and educational Center of joint use "Ground-based Astronomy" based on SAO RAS for MSU, SPbSU, KSU, RSU, UrSU and SSU student training of modern observational astronomy methods and data processing. The network will provide decision of the following tasks:
Results are presented of long-slit spectroscopy performed at BTA for three
new galaxies with a metallicity less than 1/20 of solar. The galaxies were
found from the results of the survey "The Hamburg/SAO survey
for very low metallicity BCGs" (HSS-LM). Based on high signal/noise
ratio spectra, the abundance of oxygen O/H, as well as the abundances
of the elements N, S, Ne and Ar with respect to the O abundance, was obtained.
This suggests that the enrichment of the interstellar medium in these elements
is mainly due to massive stars. Broad spectral details ("blue bamp" at
 4600-4700 A) characteristic
of Wolf-Raye (WR) stars were detected for the galaxies
4600-4700 A) characteristic
of Wolf-Raye (WR) stars were detected for the galaxies  4686
4686
Results are presented of panoramic spectroscopy of the blue compact galaxy (BCG)

 4686
4686 4686
4686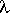 4686
4686
Model atmospheres were built for the individual components of the system
41Dra using the grid of the Kurucz (1994) blanketed models and
the entire spectral energy distribution of the system.
The fundamental parameters of the system components were
derived as:




The spectral energy distribution between
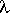 3700 AA
and
3700 AA
and
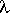 8100 AA,
of the binary systems COU 1289 and COU 1291 is presented with
a description of the methodology of
getting their spectrum on Carl-Zeiss-Jena 1 m telescope of the
Special Astrophysical Observatory. Their B,V,R magnitudes and
B-V colour indices were computed and compared with earlier
results. Model atmospheres of both systems were
constructed using the grid of the Kurucz blanketed models, and
their energy distributions in the continuous spectrum were
computed and compared with the observational ones. The model
atmosphere parameters for the components of COU1289 were derived
as:
8100 AA,
of the binary systems COU 1289 and COU 1291 is presented with
a description of the methodology of
getting their spectrum on Carl-Zeiss-Jena 1 m telescope of the
Special Astrophysical Observatory. Their B,V,R magnitudes and
B-V colour indices were computed and compared with earlier
results. Model atmospheres of both systems were
constructed using the grid of the Kurucz blanketed models, and
their energy distributions in the continuous spectrum were
computed and compared with the observational ones. The model
atmosphere parameters for the components of COU1289 were derived
as:





We present the results of the deep multicolour CCD imaging with the SAO RAS
6 m telescope of the pair of extremely metal-deficient gas-rich dwarf
galaxies SBS 0335-052 E and W.
The total magnitudes in U,B,V,R and I, and integrated fluxes
of 

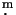 07
07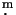 11
11
Based on high resolution spectra obtained with the
echelle-spectrometers both of the 6-m telescope of the Special
Astrophysical Observatory and of the 2-m telescope of the Terskol
Observatory, the spectral atlas of the hypergiants Cyg OB2-
No.12 (B5Ia+) and HD 168625 (B5Ia+) and of the
supergiant 67 (Oph B4Ib) was produced. The spectral range from
4790 to 6710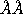 with a resolution limit 0.4
with a resolution limit 0.4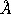 for Cyg OB2-No.12 and HD 168625 and 0.15
for Cyg OB2-No.12 and HD 168625 and 0.15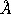 for 67 Oph is graphically presented. 330 spectral features,one third from
them - DIBs, are identified within a wavelength range of
4700-7780
for 67 Oph is graphically presented. 330 spectral features,one third from
them - DIBs, are identified within a wavelength range of
4700-7780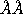 .
Relative intensities and radial velocities are presented for the spectral
details identified. The quantitave spectral classification of the
objects is made, the signs of atmospheric and wind motions -
asymmetry of profiles, differential shifts of lines and their
components - are described.
The differential shifts for 67 Oph do not exceed 2km/s within the
above-mentioned spectral region; the wind velocity up to 240km/s
and 150km/s is fixed for HD 168625 and Cyg OB2-No.12
respectively. Besides, for Cyg OB2-No.12 an envelope
compressed with a velocity of 10-15km/s is detected.
.
Relative intensities and radial velocities are presented for the spectral
details identified. The quantitave spectral classification of the
objects is made, the signs of atmospheric and wind motions -
asymmetry of profiles, differential shifts of lines and their
components - are described.
The differential shifts for 67 Oph do not exceed 2km/s within the
above-mentioned spectral region; the wind velocity up to 240km/s
and 150km/s is fixed for HD 168625 and Cyg OB2-No.12
respectively. Besides, for Cyg OB2-No.12 an envelope
compressed with a velocity of 10-15km/s is detected.
Upgrading of the efficieny of the Nasmyth-2 focus echelle spectrograph of BTA has been made of both the published and proposed by the authors engineering approaches. Reserves of upgrading the efficiency of the BTA stellar spectrographs have been considered in terms of product of throughput L into spectral resolution R. Measures have been developed and implemented for the upgrading of spectral resolution in observations with the BTA Nasmyth echelle spectrograph NES. With this end in view, an image slicer (R=7500) has been manufactured and a set of algorithms for the reduction of echelle images has been created. The method has been tested in observations. The values of R=96000 are shown to be achievable. Measures have been elaborated for the improvement of throughput in observations with the NES BTA. For this purpose, an image slicer (R=50000) tested in observations has been made. A gain in throughput by one stellar magnitude has been realized. Advantages of overfilling the echelle and application of coatings to folded flat mirrors of the collimator are considered. The total (with the image slicer) gain in the throughput is 4 times. A complex of measures has been proposed to increase the efficiency of the spectrograph LYNX: optimization of the device for the operation in the range 5500-10000A, increase in throughput owing to the overfilling of the echelle, application of coatings to the three optical surfaces, use of the image slicer. The total gain in throughput will be 3 times as high. At the same time the gain in spectral resolution will be 1.5 times as high (R=45000). The reconstruction of the spectrograph camera for the largest CCD chip of 2048 x 2048 pixels will result in increasing the number of simultaneously transmitted elements N of the spectrum by a factor of four. As a whole, the potential quality (LRN) of the spectrograph LYNX increases 18 times.
Methods of image formation in the radioheliograph mode and results of computer simulation of image deconvolution are considered. A maximum entropy method has been used for deconvolution. The quality of deconvolved images obtained with complex multibeam antenna patterns is shown to be good. The maximum entropy method is shown to enable restoration of images with a limited number of data available, a low signal-to-noise ratio and inexact antenna beam pattern.
A survey of data on optical photometry and spectroscopy of host galaxies
of gamma bursts has been accomplished. The results are presented in the
form of Hubble R-diagram. Its comparison has been made with the same
diagram derived from
the data of the deep Hubble field. An investigation has been carried
out of the inner extinction effects in host galaxies of gamma bursts. Using
broad-band BVRcIc
colours, a comparison has been made with local galaxies
having star formation bursts and the inner extinction has been estimated.
It is shown that the laws of extinction in host galaxies may be of different
form. The host galaxies (GRB 980703 and GRB 000926) have been isolated in
which the graphite absorption band at
2200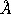 is likely to be present.
A comparison with radio data has been made for them. A method of estimation
of photometric redshifts has been applied to them and a Hubble diagram has
been construted in the B band for them. A comparison has been
performed with the
Hubble diagram for host galaxies. Some supplements for the investigation of
extinction in host galaxies are considered.
is likely to be present.
A comparison with radio data has been made for them. A method of estimation
of photometric redshifts has been applied to them and a Hubble diagram has
been construted in the B band for them. A comparison has been
performed with the
Hubble diagram for host galaxies. Some supplements for the investigation of
extinction in host galaxies are considered.
The principles of organization and the procedures of interaction of the observational databank ODA-R with the data acquisition systems of the RATAN-600 radio telescope are described. The intersystem exchange of experimental data is realized with the help of the 2-layered network buffering system ODA/BS-2L, which is a unified input interface shell of the databank.
The restoration and reorganization of the old spectral data archives of the echelle-spectrometer ZEBRA and 2x1024-channel TV photon counter system formed in the early 90s for the optical telescope BTA are described. The results of multiyear archive statistics obtained from the analyses of the created reference databases are given.
The unified local FLEX-standards designed for automatic identification of the data of the optical telescope BTA stellar spectrographs are described. The adopted convensions for name of files containing experimental data are a part of centralized descriptions in the databank ODA-B/SS.
A description of the 6-m telescope speckle interferometer is presented.
Principle of operation and function of basic units are briefly considered.
Information on the processes of observations and primary data reduction is
given. Methods of measuring binary star parameters and evaluation of the
power spectrum and image restoration are presented. It is shown that the use
of the new device gives us an opportunity to reach acquisition rate up to
6 fps, and to observe objects up to 14m with a diffraction
telescope resolution of
0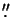 02.
02.
Optical identification of probable host galaxy of the GRB 001109 "dark" gamma-burst is made. Direct and spectral observations have been carried out. A red shift for probable host galaxy has been measured, which turned out to be z=0.398. The rate of star formation has been estimated, and the spectral energy distribution in different ranges is analysed.
In the paper there pointed upper and lower quality Hamiltonian chain estimation and Hamilton cycles on regular hypergraphs. For the validity of the upper estimation it is proposed algorithm of solving the problem on Hamiltonian chain on hypergraphs which distinguishes set of all common chains, outgoing of a fixed edge of a given hypergraph. The theorem on edge number of fu ll l-partite l-regular hypergraph, l>3, has been proved. Conditions of set Hamiltonian chain non-emptiness and Hamiltonian cycles on regular hypergraphs have been pointed out.
|