

| RUS |
|
|
|||||||||
A solution of this problem is usage of the scanning Fabry-Perot interferometer (FPI) operating in the tunable-filter mode. If the interference order is small enough, then it is easy to attain the 2-3 nm width of the instrumental profile. Along with this, the distance between neighboring interference orders in the required range is large enough, so that the rest transmission peaks if the FPI are easily cut by the medium-band filter (the bandwidth is 150-300 nm).
ET-50 piezoelectric FPI (made by IC Optical Systems Ltd, GB) with the appropriate characteristics was bought by SAO RAS within the project for the modernization of the equipment of the 6-m SAO RAS telescope ("the BTA Unique Scientific Instrument"). To effectively use the FPI when it was not involved in observations at the 6-m SAO RAS telescope, it was decided to make a guest photometer for observations on medium-sized telescopes.
The MaNGaL instrument was developed in the Laboratory of Spectroscopy and Photometry of Extragalactic Objects and manufactured in the SAO RAS workshop within the project of the Russian Science Foundation RSF 17-12-01335 "Ionized Gas in Galaxy Disks and Beyond the Optical Radius" (the project leader is Alexei Moiseev). MaNGaL is supposed to be used for observations at the 1-m SAO RAS telescope and the 2.5-m telescope of the Sternberg Astronomical Institute, Lomonosov Moscow State University to study the ionized gas state in various types of galaxies.
Results are presented at the
Russian Astronomy Conference-2017:
Perepelitsyn A.E., Moiseev A.V., "Optical Reducer with a Tunable
Interference Filter for Small- and Medium-Sized Telescopes."
Contact - Alexei Moiseev
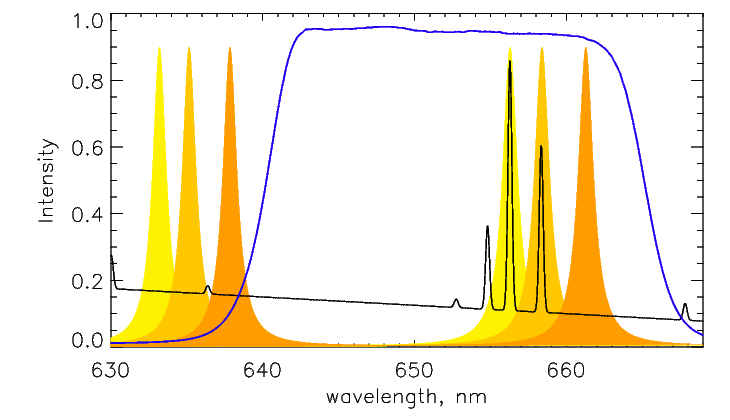
Fig.1 Tunable filter operating principle. With black, we schematically
depict the spectrum of a galaxy with bright Íα and [NII] lines.
With orange, we show the transmission profiles of the Fabry-Perot
interferometer tuned for observations in two emission lines and in the
continuum. The blue color shows the transmission curve of the medium-band
filter which gives only one transmission peak of the interferometer.
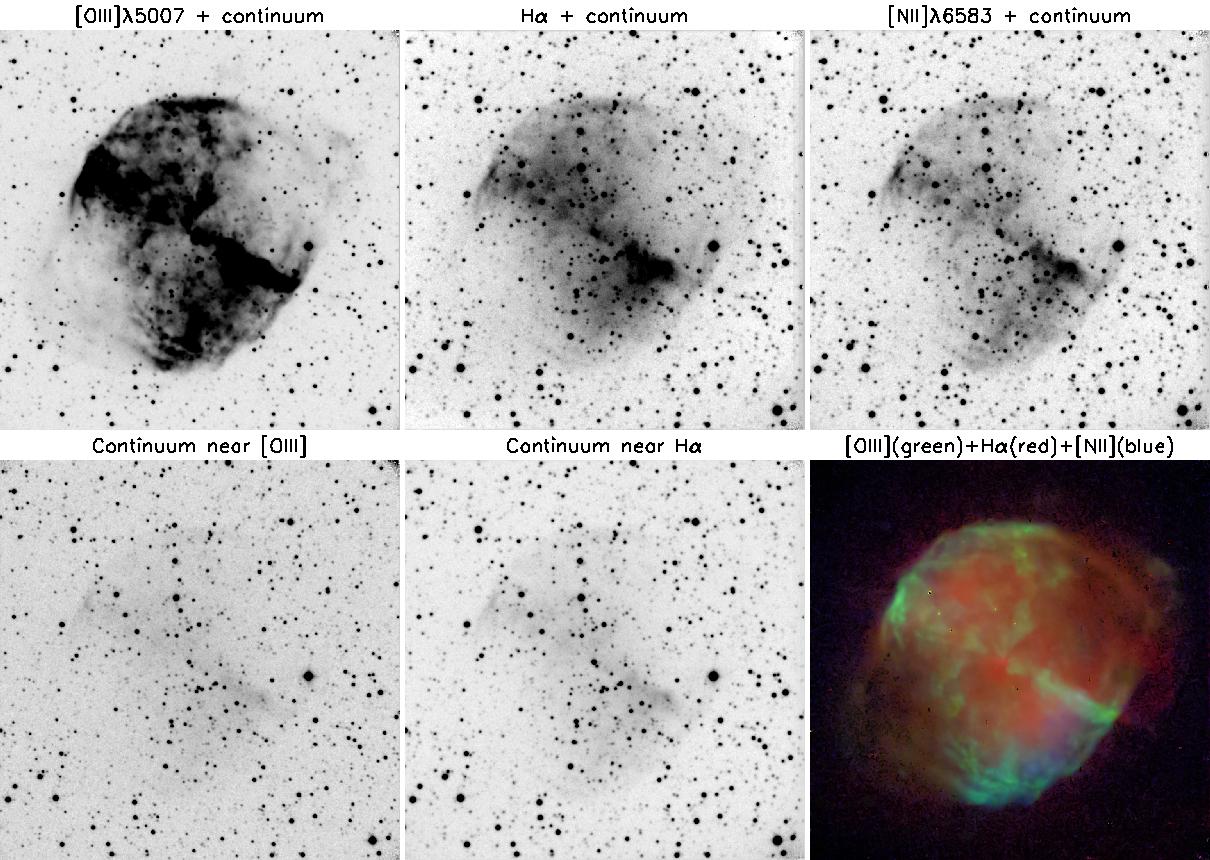
Fig.2 Images of the planetary NGC 6853 nebula in the case of the FPI
transmission peak centered at the emission lines and the continuum, as
well as the color composite image of the nebula in the [OIII], Hα
and [NII] lines after subtracting the stellar continuum.
|